इस पोस्ट में हम इलेक्ट्रिक रेसिस्टिविटी (Electric Resistivity) को परिभाषित और चर्चा करेंगे तथा इसका सूत्र (formula) निकालेंगे। एक समान मोटाई (uniform thickness) वाले दिए गए पदार्थ के एक कंडक्टर (conductor) पर विचार करें।
विस्तृत प्रयोग हमें बताते हैं कि कंडक्टर का Resistance है
(i) इसकी लंबाई (l) के सीधे आनुपातिक
(ii) इसके अनुप्रस्थ काट( cross section) के क्षेत्रफल (A) के व्युत्क्रमानुपाती (inversely propotional)।
उपरोक्त दोनों परिणामों को मिलाकर, हमारे पास है,
Resistance R समानुपाती है (l/A) के
या R = constant × (l/A)उपरोक्त समीकरण में आनुपातिकता के स्थिरांक (constant) को कंडक्टर की सामग्री की resistivity कहा जाता है और इसे ρ (ग्रीक अक्षर ‘rho’) द्वारा दर्शाया जाता है।
या R = ρ l /A
Electric Resistivity Formula
In this post, we will define and discuss Electric Resistivity, and derive its formula. Consider a conductor of a given material having a uniform thickness.
Detailed experiments tell us that the resistance of the conductor is
(i) directly proportional to its length (l)
(ii) inversely proportional to its area of cross-section (A).
Combining the above two results, we have,
R is proportional to (l/A)
or R = constant × (l/A)
The constant of proportionality is called the resistivity of the material of the conductor and is denoted by ρ (Greek letter ‘rho’).
So,
R = ρ l /A ……………… (1)
Resistivity Formula (deriving from the resistance equation)
From Equation 1 above, we can also write the expression of resistivity in the following way:
Resistivity ρ = R A/l
Resistivity Definition
In Eq. (1) above, let A = 1 unit, l =1 unit, then ρ = R
Therefore, the resistivity of a material is numerically equal to the resistance per unit length of a uniform conductor of that material having a unit area of cross-section.
इसलिए, किसी सामग्री की resistivity संख्यात्मक रूप से क्रॉस-सेक्शन के एक इकाई क्षेत्र वाले उस सामग्री के uniform कंडक्टर की प्रति इकाई लंबाई के resistance के बराबर होती है।
Resistivity is an important property of the material of the conductor.
Resistivity value is independent of the physical dimensions of the conductor but varies with temperature.
Unit of resistivity
By rewriting Eq. (1) as ρ = R A/l and substituting the SI units of resistance R as ohm, area A as (meter)2, and length l as meter respectively, we find that the SI unit of resistivity is ohm meter (or Ω m).
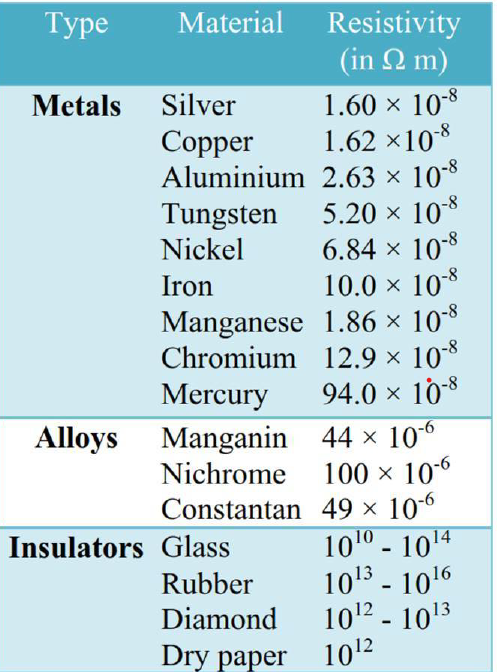
Resistivity values of some important substances
The resistivity values of some important substances are given in the Table below.
The resistivity of a substance varies with temperature. The listed values in the table correspond to a temperature of 200 C.